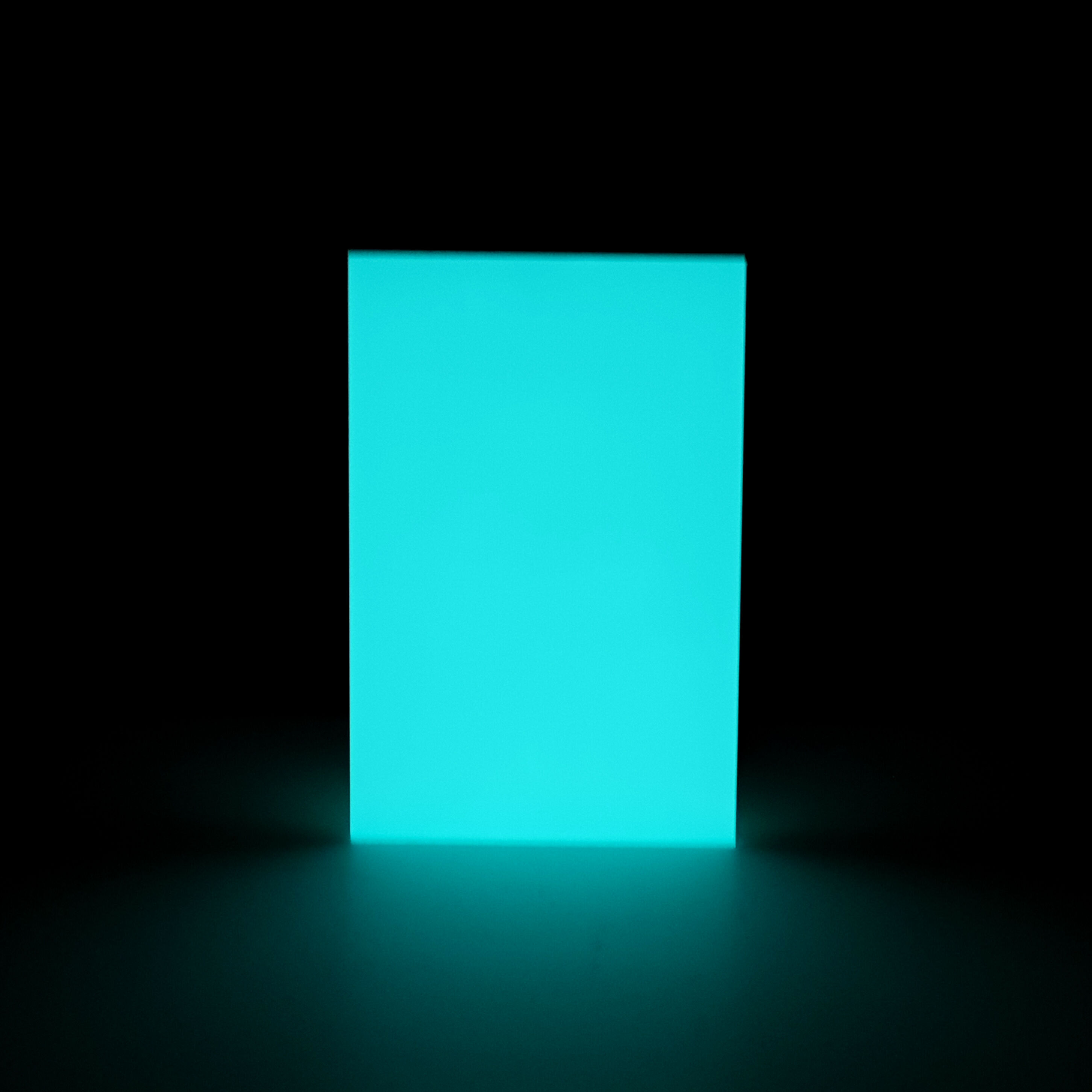
In the fascinating world of photoluminescent materials, strontium aluminate glow powder stands as one of the most remarkable innovations in modern chemistry and materials science. This revolutionary compound has transformed countless industries by providing long-lasting, brilliant luminescence that far surpasses traditional phosphorescent materials. Understanding how strontium aluminate glow powder functions requires delving into the intricate quantum mechanical processes that occur at the atomic level, where energy absorption and emission create the mesmerizing glow effect that has captivated scientists and manufacturers alike.
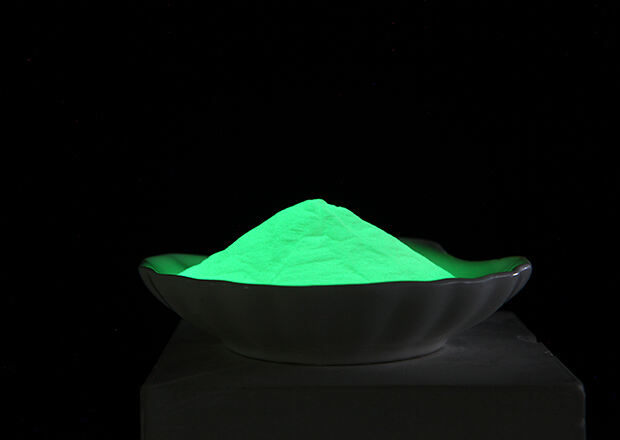

The exceptional properties of strontium aluminate glow powder have made it indispensable across numerous applications, from safety signage and emergency lighting systems to decorative coatings and industrial markings. Unlike its predecessor zinc sulfide, this advanced phosphorescent material offers superior brightness intensity, extended glow duration, and enhanced chemical stability. The scientific principles governing its luminescent behavior involve complex interactions between dopant ions, crystal lattice structures, and electromagnetic radiation that create a sustainable energy storage and release mechanism.
The Chemical Composition and Crystal Structure
Fundamental Chemical Properties
The chemical foundation of strontium aluminate glow powder lies in its sophisticated molecular structure, typically represented as SrAl₂O₄. This alkaline earth aluminate compound forms a robust crystalline matrix that serves as the host material for activator and co-activator ions. The strontium ions occupy specific lattice positions within the crystal structure, creating an environment conducive to photoluminescent behavior when combined with carefully selected dopant materials.
The crystal lattice of strontium aluminate glow powder exhibits a monoclinic structure at room temperature, which provides optimal geometric arrangements for efficient energy transfer processes. This crystalline framework contains numerous defect sites and interstitial positions where dopant ions can be incorporated during the synthesis process. The precise arrangement of atoms within the lattice directly influences the material's ability to absorb, store, and emit light energy over extended periods.
Role of Dopant Ions
Europium and dysprosium ions serve as the primary activators in high-performance strontium aluminate glow powder formulations. Europium ions, typically present in the divalent state (Eu²⁺), act as the primary luminescent centers responsible for the characteristic green emission observed in most commercial products. These ions substitute for strontium ions within the crystal lattice, creating localized energy states that facilitate the photoluminescent process.
Dysprosium ions function as co-activators or sensitizers, enhancing the overall performance characteristics of the strontium aluminate glow powder. These trivalent ions (Dy³⁺) create trap states within the material's energy band structure, effectively increasing the duration of the afterglow effect. The synergistic interaction between europium and dysprosium ions produces the superior luminescent properties that distinguish modern phosphorescent materials from earlier alternatives.
The Photoluminescent Mechanism
Energy Absorption Process
The luminescent cycle of strontium aluminate glow powder begins with the absorption of excitation energy from external light sources. When photons with sufficient energy strike the material's surface, they interact with the dopant ions embedded within the crystal lattice. This initial energy absorption process involves the promotion of electrons from their ground state energy levels to higher excited states, creating electron-hole pairs within the phosphorescent matrix.
The efficiency of energy absorption in strontium aluminate glow powder depends on several factors, including the wavelength of incident light, the concentration of activator ions, and the crystal quality of the host material. Optimal charging occurs under broad-spectrum illumination, with peak absorption typically observed in the ultraviolet and blue regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. The material can effectively capture and store energy from various artificial and natural light sources, making it highly versatile for practical applications.
Trap State Formation and Energy Storage
Following the initial energy absorption, strontium aluminate glow powder utilizes sophisticated trap mechanisms to store excitation energy for extended periods. The dysprosium co-activator ions create discrete energy levels within the material's band gap, functioning as temporary storage sites for excited electrons. These trap states exhibit varying depths, allowing for controlled energy release over time scales ranging from minutes to hours.
The trap state distribution in strontium aluminate glow powder follows a complex energy landscape that governs the temporal characteristics of the afterglow phenomenon. Shallow traps contribute to the initial bright emission immediately following excitation, while deeper trap levels sustain the long-term luminescent output. This hierarchical energy storage system enables the material to provide sustained illumination long after the excitation source has been removed.
Emission Characteristics and Spectral Properties
Wavelength Distribution and Color Output
The emission spectrum of strontium aluminate glow powder is characterized by distinct peaks that correspond to specific electronic transitions within the europium activator ions. The primary emission band typically occurs around 520 nanometers, producing the characteristic yellow-green color that provides optimal visibility to the human eye. This wavelength corresponds to the maximum sensitivity of human photopic vision, making strontium aluminate glow powder particularly effective for safety and emergency applications.
Advanced formulations of strontium aluminate glow powder can be engineered to produce alternative emission colors through careful modification of the dopant ion concentrations and host matrix composition. Blue, aqua, and purple variants are achieved by incorporating different activator species or adjusting the crystal field environment surrounding the luminescent centers. These spectral variations expand the application possibilities while maintaining the fundamental photoluminescent mechanisms that define the material's performance.
Temporal Decay Characteristics
The afterglow duration of strontium aluminate glow powder follows a characteristic decay profile that reflects the complex trap state dynamics within the material. Initial brightness levels immediately after excitation can exceed 300 millicandelas per square meter, providing intense illumination comparable to conventional lighting sources. The subsequent decay typically follows multiple exponential components, with different time constants governing short-term and long-term emission phases.
High-quality strontium aluminate glow powder formulations can maintain visible luminescence for over 12 hours following a brief charging period under standard illumination conditions. The practical visibility duration depends on environmental factors such as ambient light levels, viewing conditions, and the observer's dark adaptation state. This extended performance capability represents a significant advancement over traditional zinc sulfide phosphors, which typically exhibit much shorter afterglow durations.
Manufacturing Processes and Quality Control
Synthesis Methods and Production Techniques
The production of high-quality strontium aluminate glow powder requires sophisticated manufacturing processes that ensure optimal crystal formation and dopant incorporation. Solid-state reaction methods remain the most common approach, involving high-temperature calcination of precisely mixed raw materials in controlled atmospheric conditions. The synthesis temperature typically ranges from 1200 to 1400 degrees Celsius, allowing for complete reaction and proper crystal development.
Alternative production methods for strontium aluminate glow powder include sol-gel processing, combustion synthesis, and co-precipitation techniques. These approaches offer advantages in terms of particle size control, morphology optimization, and chemical homogeneity. The choice of synthesis method significantly influences the final product characteristics, including brightness intensity, afterglow duration, and physical stability under various environmental conditions.
Quality Assessment and Performance Standards
Rigorous quality control measures are essential for ensuring consistent performance in commercial strontium aluminate glow powder products. Standard testing protocols evaluate key parameters such as initial brightness, afterglow duration, particle size distribution, and chemical purity. These assessments utilize specialized photometric equipment and standardized measurement conditions to provide reliable performance data for end users.
Long-term stability testing of strontium aluminate glow powder involves exposure to various environmental stressors, including elevated temperatures, humidity cycles, and ultraviolet radiation. These accelerated aging studies help predict the material's performance under real-world conditions and establish appropriate storage and handling recommendations. Quality specifications typically include minimum brightness levels, decay time constants, and particle size ranges that ensure optimal performance in target applications.
Industrial Applications and Market Sectors
Safety and Emergency Systems
The superior performance characteristics of strontium aluminate glow powder have made it the material of choice for critical safety and emergency applications. Photoluminescent exit signs, emergency evacuation markings, and safety pathway systems rely on the extended afterglow duration to provide reliable illumination during power outages or emergency situations. The material's ability to function without electrical power makes it invaluable for building safety compliance and emergency preparedness.
Marine and aviation industries have adopted strontium aluminate glow powder for various safety-critical applications, including life vest markers, emergency equipment identification, and instrument panel illumination. The material's resistance to moisture and temperature variations ensures reliable performance in challenging environmental conditions. Additionally, the non-toxic nature of strontium aluminate glow powder makes it suitable for applications where human contact is possible.
Consumer and Decorative Markets
Beyond safety applications, strontium aluminate glow powder has found extensive use in consumer products and decorative applications. Novelty items, toys, and craft materials utilize the material's captivating glow effect to create visually striking products that appeal to diverse market segments. The ability to incorporate the powder into various substrates, including plastics, paints, and textiles, provides manufacturers with significant design flexibility.
Architectural and landscape lighting applications increasingly incorporate strontium aluminate glow powder to create energy-efficient illumination solutions. Decorative concrete, paving stones, and building materials embedded with phosphorescent particles provide ambient lighting without ongoing energy consumption. These applications demonstrate the material's potential for sustainable design solutions that combine aesthetic appeal with functional performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ecological Benefits and Green Technology
The environmental advantages of strontium aluminate glow powder stem from its ability to provide illumination without consuming electrical energy during the emission phase. This characteristic makes it an attractive option for reducing energy consumption in various applications, particularly in emergency lighting systems that traditionally relied on battery-powered LED arrays. The passive nature of photoluminescent technology contributes to lower carbon footprints and reduced environmental impact.
Unlike some traditional luminescent materials, strontium aluminate glow powder contains no radioactive components or heavy metals that pose environmental hazards. The inorganic composition ensures long-term chemical stability and prevents the release of toxic substances during normal use or disposal. This environmental compatibility supports the growing demand for sustainable materials in commercial and industrial applications.
Lifecycle Assessment and Disposal Considerations
Comprehensive lifecycle assessments of strontium aluminate glow powder reveal favorable environmental profiles compared to alternative lighting technologies. The manufacturing process, while energy-intensive due to high-temperature synthesis requirements, produces materials with exceptionally long service lives that offset the initial environmental investment. The absence of moving parts or degradable components ensures minimal maintenance requirements throughout the product lifecycle.
End-of-life disposal of strontium aluminate glow powder presents minimal environmental concerns due to the material's chemical inertness and non-toxic composition. Standard waste management practices can accommodate phosphorescent materials without special handling procedures or environmental precautions. The potential for recycling and material recovery further enhances the sustainability profile of strontium aluminate glow powder applications.
Future Developments and Research Directions
Advanced Material Formulations
Ongoing research in strontium aluminate glow powder technology focuses on developing enhanced formulations with improved performance characteristics. Novel dopant combinations and crystal engineering approaches promise to extend afterglow durations, increase brightness levels, and expand the available emission color palette. These advances could enable new applications in specialized sectors such as medical imaging, security printing, and advanced display technologies.
Nanotechnology applications present exciting opportunities for strontium aluminate glow powder development, including nanoparticle formulations with tailored optical properties and surface modifications for specific applications. These advanced materials could provide enhanced performance in thin-film applications, composite materials, and integration with electronic systems. The potential for smart materials that respond to environmental stimuli represents a frontier area for future innovation.
Emerging Applications and Market Opportunities
The expanding application landscape for strontium aluminate glow powder includes emerging sectors such as wearable technology, smart textiles, and biomedical devices. Integration with flexible substrates and electronic systems opens possibilities for innovative product designs that combine phosphorescent functionality with digital technologies. These hybrid applications could revolutionize fields ranging from personal safety equipment to interactive displays.
Space and aerospace applications present unique opportunities for strontium aluminate glow powder utilization, where reliable emergency lighting systems must function in extreme environments without electrical power. The material's radiation resistance and temperature stability make it suitable for mission-critical applications in spacecraft, satellites, and space exploration equipment. These specialized applications drive continued research into material optimization and performance enhancement.
FAQ
How long does strontium aluminate glow powder maintain its luminescence after charging
High-quality strontium aluminate glow powder can maintain visible luminescence for 12 to 24 hours after a brief charging period under standard lighting conditions. The exact duration depends on factors such as the powder grade, particle size, charging time, and ambient lighting conditions. Professional-grade formulations designed for safety applications typically provide at least 10 hours of practical visibility, meeting international standards for emergency lighting systems.
What is the difference between strontium aluminate and zinc sulfide glow powders
Strontium aluminate glow powder offers significantly superior performance compared to traditional zinc sulfide phosphors in terms of brightness intensity, afterglow duration, and chemical stability. While zinc sulfide typically provides 1-3 hours of visible luminescence, strontium aluminate can glow for over 12 hours. Additionally, strontium aluminate exhibits better resistance to moisture and UV degradation, making it more suitable for outdoor and long-term applications.
Can strontium aluminate glow powder be mixed with different materials and coatings
Yes, strontium aluminate glow powder demonstrates excellent compatibility with various binder systems, including acrylic paints, epoxy resins, silicone compounds, and thermoplastic materials. The powder can be incorporated into coatings, plastics, ceramics, and textiles while maintaining its photoluminescent properties. Proper dispersion techniques and appropriate powder concentrations are essential for achieving optimal performance and uniform glow distribution in the final product.
Is strontium aluminate glow powder safe for human contact and environmental exposure
Strontium aluminate glow powder is considered safe for human contact and environmental exposure when used as intended. The material contains no radioactive components or toxic heavy metals, making it suitable for applications where incidental human contact may occur. The inorganic composition ensures chemical stability and prevents the release of harmful substances under normal use conditions. However, as with any fine powder, appropriate dust control measures should be implemented during handling and processing to avoid respiratory irritation.
Table of Contents
- The Chemical Composition and Crystal Structure
- The Photoluminescent Mechanism
- Emission Characteristics and Spectral Properties
- Manufacturing Processes and Quality Control
- Industrial Applications and Market Sectors
- Environmental Impact and Sustainability
- Future Developments and Research Directions
-
FAQ
- How long does strontium aluminate glow powder maintain its luminescence after charging
- What is the difference between strontium aluminate and zinc sulfide glow powders
- Can strontium aluminate glow powder be mixed with different materials and coatings
- Is strontium aluminate glow powder safe for human contact and environmental exposure