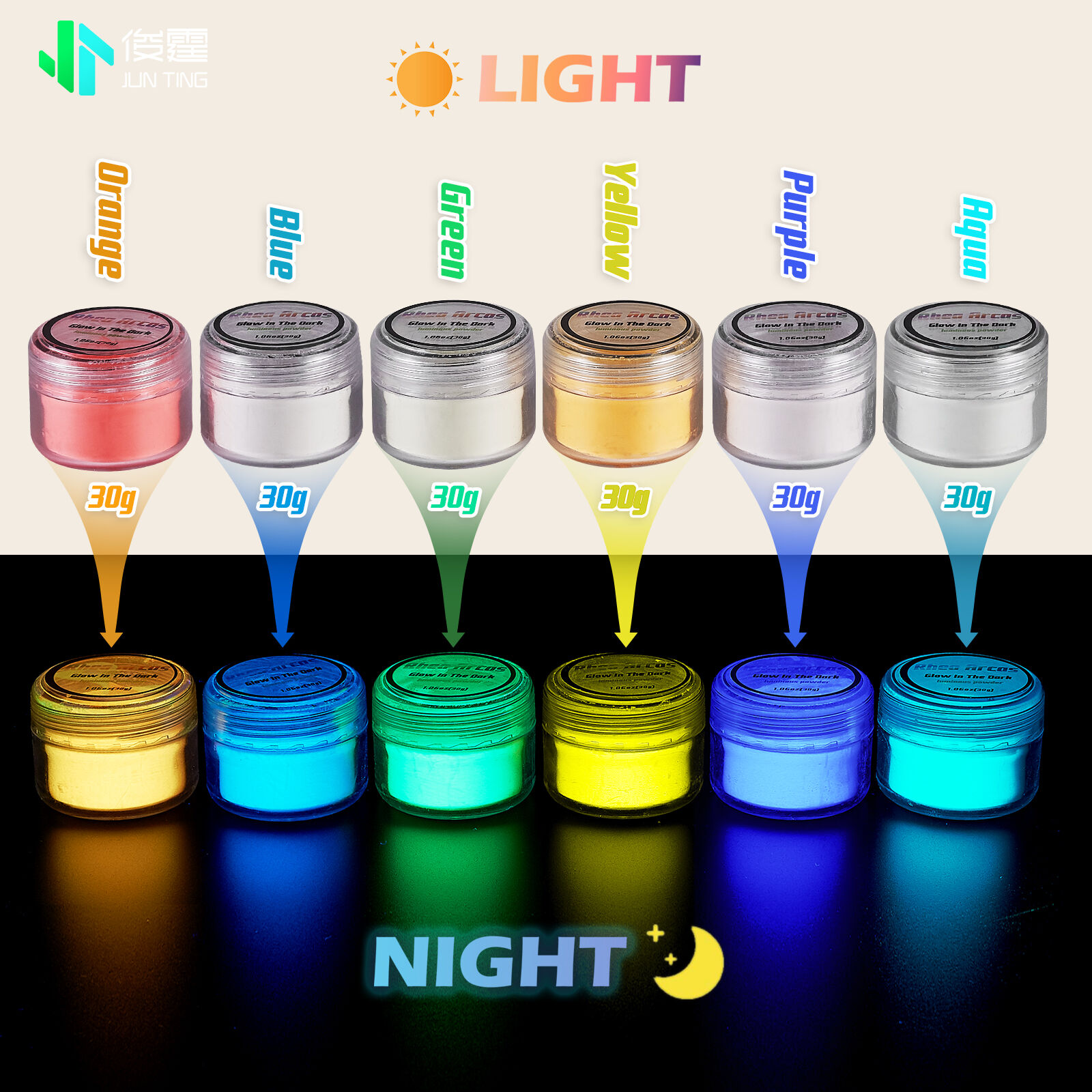
Photoluminescent pigment represents a revolutionary advancement in luminous technology that has transformed industries ranging from safety signage to decorative arts. This remarkable material absorbs light energy and releases it gradually in dark conditions, creating a sustainable glow-in-the-dark effect without requiring external power sources. Understanding photoluminescent pigment properties, applications, and manufacturing processes helps professionals make informed decisions about incorporating this innovative technology into their projects.

The science behind photoluminescent pigment involves complex photophysical processes where specialized compounds store photon energy and release it through phosphorescence. Modern manufacturing techniques have significantly improved the brightness, duration, and stability of these materials, making them increasingly valuable for commercial and industrial applications. Today's advanced formulations offer superior performance characteristics compared to traditional luminous materials, providing longer afterglow periods and enhanced durability.
Fundamental Properties and Composition
Chemical Structure and Base Materials
The foundation of effective photoluminescent pigment lies in rare earth elements, particularly europium and dysprosium, which serve as activators in alkaline earth aluminate host matrices. Strontium aluminate and calcium aluminate represent the most common host materials, offering excellent luminous efficiency and chemical stability. These compounds undergo careful synthesis processes where precise temperature control and atmospheric conditions determine the final product quality.
Manufacturing excellence requires maintaining strict quality control throughout the production process, ensuring consistent particle size distribution and optimal crystalline structure formation. The incorporation of co-activators like neodymium enhances the charging efficiency and extends the afterglow duration significantly. Advanced photoluminescent pigment formulations achieve brightness levels exceeding 300 millicandela per square meter after ten minutes of darkness, representing substantial improvements over earlier generations.
Optical Characteristics and Performance Metrics
Excitation wavelengths for high-quality photoluminescent pigment typically range from 200 to 450 nanometers, with peak absorption occurring around 365 nanometers in the ultraviolet spectrum. The emission characteristics show maximum intensity at approximately 520 nanometers, producing the characteristic blue-green glow that provides optimal visibility to the human eye. These spectral properties ensure efficient charging under various lighting conditions including natural daylight, fluorescent, and LED illumination.
Afterglow duration represents a critical performance parameter, with premium grades maintaining visible luminosity for over 12 hours following a brief charging period. The decay curve follows predictable patterns that allow engineers to calculate visibility requirements for specific applications. Temperature stability ensures consistent performance across environmental conditions, with quality photoluminescent pigment maintaining effectiveness from -40°C to +80°C without degradation.
Manufacturing Processes and Quality Control
Production Techniques and Equipment
State-of-the-art manufacturing facilities employ high-temperature solid-state reaction methods to produce superior photoluminescent pigment with consistent quality characteristics. The process begins with precise weighing and mixing of raw materials, followed by calcination at temperatures exceeding 1300°C in controlled atmospheric conditions. This thermal treatment creates the crystalline structure necessary for efficient photon absorption and emission.
Quality assurance protocols include comprehensive testing of luminous intensity, particle size distribution, and chemical purity at multiple production stages. Advanced grinding and classification equipment ensures uniform particle sizes that optimize dispersion characteristics in various carrier systems. The final product undergoes rigorous testing for brightness decay curves, weather resistance, and chemical stability before packaging and distribution.
Surface Treatment and Stabilization
Modern photoluminescent pigment receives specialized surface treatments to enhance durability and compatibility with different matrix materials. Silane coupling agents improve adhesion to polymer systems while providing moisture resistance that extends service life. These treatments also reduce particle agglomeration during storage and processing, ensuring consistent dispersion characteristics.
Encapsulation technologies protect the active luminous compounds from environmental degradation, particularly moisture and acidic conditions that can compromise performance. Advanced coating systems maintain the optical properties while improving handling characteristics and reducing dust formation during manufacturing processes. These innovations have significantly expanded the application range for photoluminescent pigment in demanding industrial environments.
Applications Across Industries
Safety and Emergency Systems
Emergency egress systems represent one of the most critical applications for photoluminescent pigment, providing reliable wayfinding during power outages or emergency situations. Building codes increasingly recognize the value of photoluminescent materials for exit signs, pathway markings, and stairwell identification systems. These installations offer significant advantages over electrically powered emergency lighting, including reduced maintenance costs and elimination of battery replacement requirements.
Maritime and aviation industries utilize photoluminescent pigment for safety equipment marking, instrument panel illumination, and emergency equipment identification. The self-powered nature of these materials ensures functionality even when electrical systems fail, providing crucial visibility for safety-critical operations. Compliance with international safety standards requires specific brightness levels and duration specifications that modern formulations readily achieve.
Decorative and Architectural Applications
Architectural designers increasingly incorporate photoluminescent pigment into concrete, terrazzo, and coating systems to create stunning visual effects while providing functional illumination. Decorative applications range from artistic installations to practical pathway lighting that enhances safety without energy consumption. The versatility of these materials allows integration into various architectural elements including pavement surfaces, wall treatments, and landscape features.
Interior design applications leverage photoluminescent pigment to create ambient lighting effects, novelty items, and educational displays. The material's ability to charge from ambient lighting makes it ideal for residential and commercial spaces where conventional lighting may be impractical or undesirable. Modern formulations offer improved color stability and reduced yellowing, maintaining aesthetic appeal over extended periods.
Technical Specifications and Performance Standards
Brightness and Duration Requirements
International standards define specific performance criteria for photoluminescent pigment used in safety applications, including minimum brightness levels after specified charging and darkness periods. DIN 67510 and ASTM E2072 provide comprehensive testing protocols that ensure consistent quality and reliability across different manufacturers and applications. These standards specify measurement procedures, environmental testing requirements, and acceptable performance thresholds.
Commercial grade photoluminescent pigment typically achieves initial brightness levels of 1000-3000 millicandela per square meter, declining to measurable levels after 10-12 hours of darkness. Premium grades exceed these baseline requirements significantly, offering enhanced performance for demanding applications. Regular testing protocols verify that production batches meet specified criteria before release to customers.
Environmental Resistance and Durability
Weather resistance testing evaluates photoluminescent pigment performance under accelerated aging conditions including UV exposure, temperature cycling, and humidity variations. Quality materials maintain luminous efficiency exceeding 80% of initial values after 1000 hours of weathering tests. Chemical resistance ensures compatibility with various matrix materials and prevents degradation from common environmental contaminants.
Long-term stability studies demonstrate that properly formulated photoluminescent pigment retains functional performance for decades under normal service conditions. The crystalline structure of alkaline earth aluminates provides inherent stability against thermal cycling and mechanical stress. These characteristics make the material suitable for permanent installations where maintenance access is limited or costly.
Integration Methods and Processing Techniques
Dispersion in Polymer Systems
Successful integration of photoluminescent pigment into polymer matrices requires careful attention to processing conditions, particle loading levels, and compatibility factors. Typical loading concentrations range from 10-30% by weight, depending on the desired brightness level and application requirements. Higher concentrations may affect mechanical properties of the host material, requiring optimization studies to balance luminous performance with structural integrity.
Processing temperature limitations protect the photoluminescent pigment from thermal degradation during manufacturing operations. Most formulations tolerate temperatures up to 200-250°C for limited periods, making them compatible with common thermoplastic processing methods. Proper dispersion techniques ensure uniform distribution throughout the matrix material, preventing agglomeration that could compromise optical performance.
Coating and Paint Formulations
Paint and coating systems incorporating photoluminescent pigment require specialized formulation approaches to achieve optimal performance characteristics. Binder selection affects both the optical properties and durability of the finished coating, with acrylic and polyurethane systems offering excellent results for most applications. Particle settling during storage necessitates appropriate rheology modifiers and suspension agents.
Application techniques significantly influence the final brightness and uniformity of photoluminescent coatings. Spray application typically provides the most consistent results, while brush and roller methods require careful technique to prevent streaking or uneven coverage. Dry film thickness directly correlates with brightness levels, requiring precise control to meet performance specifications while managing material costs effectively.
Quality Assessment and Testing Procedures
Laboratory Testing Protocols
Comprehensive quality assessment of photoluminescent pigment involves multiple testing procedures that evaluate both immediate performance and long-term stability characteristics. Initial brightness measurements utilize calibrated photometers under standardized charging and measurement conditions. These tests establish baseline performance data that enables comparison between different grades and suppliers.
Particle size analysis confirms that the material meets specifications for the intended application, as particle distribution affects both optical properties and processing characteristics. X-ray diffraction studies verify the crystalline structure and phase purity that determine luminous efficiency. Chemical analysis ensures absence of heavy metals and other contaminants that could affect safety or environmental compliance.
Field Performance Evaluation
Real-world testing provides valuable data on how photoluminescent pigment performs under actual service conditions, including variable lighting environments and weather exposure. Field installations allow evaluation of charging efficiency under different light sources and seasonal variations. Long-term monitoring reveals any degradation trends that may not be apparent in accelerated laboratory testing.
Performance documentation includes brightness measurements at regular intervals, visual assessments of uniformity and color stability, and evaluation of any physical changes in the material or matrix system. This data helps establish realistic service life expectations and maintenance requirements for specific applications. Feedback from field testing often drives improvements in formulation and processing techniques.
Future Developments and Innovations
Advanced Material Formulations
Research continues to improve photoluminescent pigment performance through novel host materials, enhanced activator systems, and improved surface treatments. Nanoscale engineering approaches offer potential for increased brightness and extended duration characteristics. New synthesis methods may enable production of materials with customized emission colors and improved environmental stability.
Hybrid systems combining photoluminescent pigment with other functional materials create opportunities for multifunctional applications. Integration with thermochromic or photochromic compounds could produce materials that respond to multiple environmental stimuli. Smart material concepts may incorporate photoluminescent pigment into responsive systems that adapt to changing conditions automatically.
Emerging Application Areas
Textile applications represent a growing market for photoluminescent pigment, with development of fiber treatments and fabric coatings that provide safety visibility for workwear and recreational clothing. Automotive applications include interior trim elements, safety equipment marking, and emergency access indicators. The transportation industry continues to explore new uses for these materials in railway systems, airport infrastructure, and marine applications.
Consumer electronics and household products increasingly incorporate photoluminescent pigment for functional and aesthetic purposes. Energy storage research investigates methods to extend charging retention and improve efficiency under low-light conditions. These developments promise to expand the practical utility of photoluminescent materials in everyday applications.
FAQ
How long does photoluminescent pigment glow in complete darkness
High-quality photoluminescent pigment can maintain visible luminosity for 8-12 hours after being charged with light for just 10-15 minutes. The brightness gradually decreases over time, with the most intense glow occurring in the first hour after the light source is removed. Premium grades may show detectable luminosity for up to 24 hours under ideal conditions, though practical visibility typically lasts 10-12 hours for most applications.
What factors affect the brightness and duration of photoluminescent materials
Several factors influence performance including the intensity and duration of charging light, particle size and concentration in the matrix material, temperature conditions, and the quality of the base formulation. UV and visible light provide the most effective charging, while particle loading levels between 15-25% typically optimize brightness without compromising the host material properties. Environmental factors like humidity and chemical exposure can gradually reduce performance over time.
Can photoluminescent pigment be mixed with different types of paints and coatings
Yes, photoluminescent pigment is compatible with most water-based and solvent-based coating systems including acrylics, polyurethanes, epoxies, and alkyd paints. However, the binder system affects both the optical properties and durability of the finished coating. Transparent or lightly pigmented base materials provide the best results, while dark or heavily pigmented systems may block light transmission and reduce charging efficiency. Processing temperatures should remain below 250°C to prevent thermal damage to the luminous properties.
Is photoluminescent pigment safe for use in consumer products and food contact applications
Modern photoluminescent pigment formulations are non-toxic and contain no radioactive materials, making them safe for most consumer applications when properly encapsulated in suitable matrix materials. However, direct food contact applications require special food-grade formulations and appropriate regulatory approvals. The materials are chemically inert under normal conditions and do not release harmful substances during typical use. Safety data sheets and regulatory compliance documentation should be reviewed for specific applications and jurisdictions.
Table of Contents
- Fundamental Properties and Composition
- Manufacturing Processes and Quality Control
- Applications Across Industries
- Technical Specifications and Performance Standards
- Integration Methods and Processing Techniques
- Quality Assessment and Testing Procedures
- Future Developments and Innovations
-
FAQ
- How long does photoluminescent pigment glow in complete darkness
- What factors affect the brightness and duration of photoluminescent materials
- Can photoluminescent pigment be mixed with different types of paints and coatings
- Is photoluminescent pigment safe for use in consumer products and food contact applications